Analysis of Poiseuille Flow In Rectangular Duct vs. Infinitely Large Flat Plates
Project Summary
- My senior capstone design team needed to characterize the flow within our system in order to build a physical model visualizing Poiseuille flow between infinitely large flat plates.
Analysis Steps
- The intended design was simplified into key geometric properties describing a system where a pump drives the movement of a water-glycerin mixture through pipes into a sealed rectangular pipe.
- The inputs (our design needs) were defined to ensure incompressible, Newtonian, laminar fluid flow in a reasonable size range.
- The outputs (in terms of velocity, volumetric flow rate, and pump delivery pressure) were calculated using fluid mechanics concepts.

MATLAB live script code snippet.
Challenges
- Since infinitely large flat plates are not possible to build and our maximum size range is something that can fit through doors, we needed to ensure that flow within a rectangular duct could approximate flow between infinite plates. Calculations were done for both scenarios and compared.
- To ensure laminar flow, the Reynold’s number was set to a low value. This made the resulting velocity very low, which required the viscosity of the mixture to be adjusted with various proportions of water and glycerin.
Results
- MATLAB was used to document the analysis, allowing the capstone team to adjust the input parameters until a desired set of output parameters were achieved. This analysis drives all the key components of the design: the dimensions, the materials, and the pump.
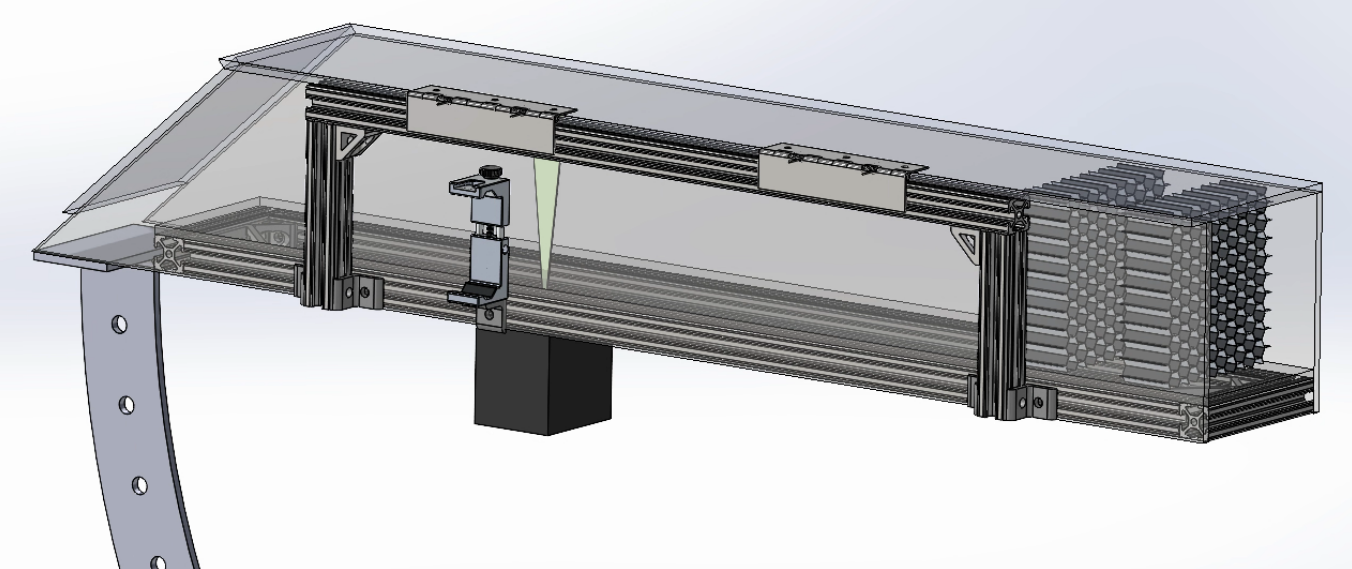
Resulting analysis-driven CAD.
Skills Developed
- Using mechanical engineering concepts to drive and justify design decisions
- Simplifying complex systems for mathematical analysis
Additional Info
- The MATLAB Live script can be downloaded here.